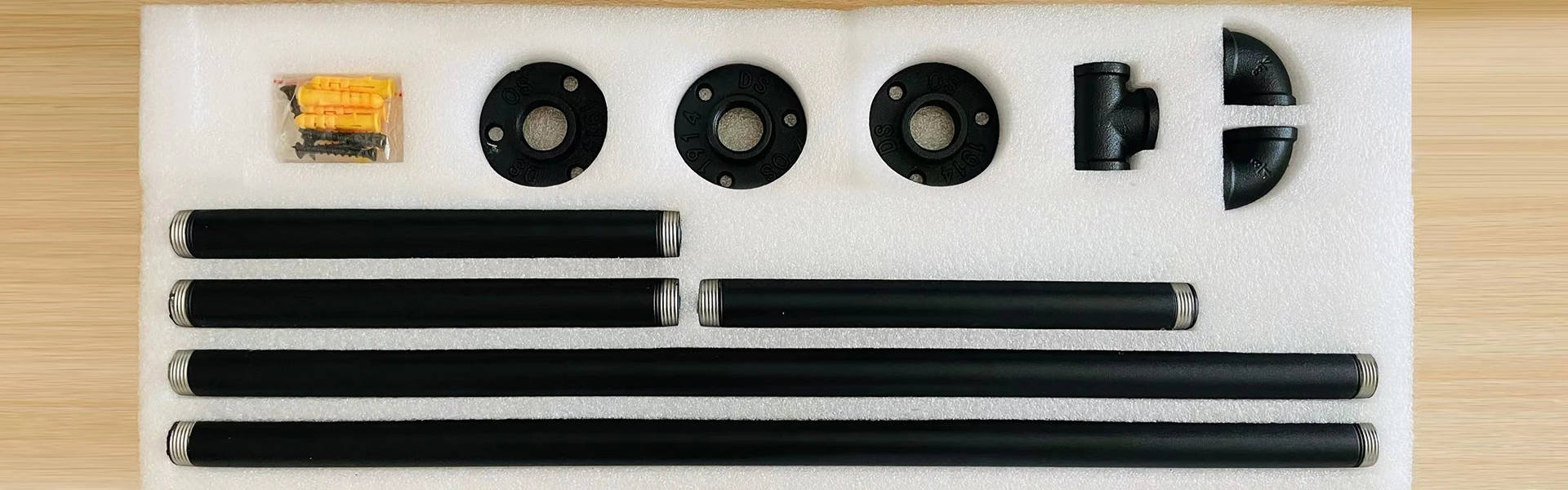
-
 Mail Usadmin1@hanghongtrade.com
Mail Usadmin1@hanghongtrade.com -
 Call Us+8613313271100
Call Us+8613313271100 -
language
okt . 10, 2024 15:11 Back to list
black iron vs cast iron factories
Black Iron vs. Cast Iron A Comparative Analysis of Factories
In the world of metallurgy and manufacturing, iron plays a crucial role in various industrial applications. Among the types of iron used, black iron and cast iron are two of the most prominent. They are used across numerous industries, including construction, automotive, and manufacturing, each possessing unique properties which determine their suitability for specific applications. Understanding the differences between these two types of iron, particularly in the context of their production in factories, is essential for anyone involved in industrial processes or seeking to optimize their production line.
Understanding Black Iron and Cast Iron
Before delving into the differences in manufacturing processes and applications, it’s essential to define black iron and cast iron. Black iron typically refers to mild steel that has not undergone any surface treatment, often appearing in a raw, dark finish. It presents excellent malleability and ductility, making it ideal for various applications, including construction scaffolding, flat sheets, and pipes.
On the other hand, cast iron is an alloy of iron that contains a high percentage of carbon (usually between 2% to 4%). It comes in several forms, the most common being gray cast iron, ductile cast iron, and white cast iron. Cast iron is known for its brittleness, high wear resistance, and excellent casting properties, making it suitable for manufacturing items such as engine blocks, cookware, and pipes.
Manufacturing Processes in Factories
The production processes for black iron and cast iron vary significantly, reflecting the different properties they possess.
1. Manufacturing Black Iron Black iron is produced primarily through the process of steel-making. This involves melting iron ore in electric arc furnaces (EAF) or basic oxygen furnaces (BOF). The steel is then refined, which includes the removal of impurities and the addition of alloys. This process allows the manufacturers to control the properties of mild steel closely. Black iron is typically available in various forms such as sheets, bars, and pipes, allowing for versatile manufacturing and construction applications.
black iron vs cast iron factories
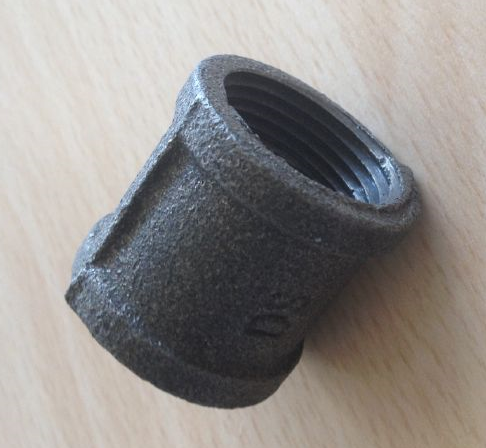

Factories that produce black iron often focus on high-speed production techniques, utilizing automation to maximize output and maintain structural integrity
. Given its relatively low cost and high availability, factories are often optimized for efficient mass production methods.2. Manufacturing Cast Iron The production of cast iron involves a different approach, centered around the melting and casting process. It starts with melting pig iron, scrap iron, and various alloys in a cupola furnace or induction furnace. Once the desired temperature is reached, the molten iron is poured into molds to form various cast products.
The casting process requires careful control over temperature and molding techniques, as these factors significantly influence the quality of the final product. Cast iron foundries focus on the intricacies of mold design, cooling rates, and alloy composition to achieve superior mechanical properties—traits desired in products such as heavy machinery components or decorative castings.
Applications and Industry Utilization
The differences in their production processes lead to distinct applications for black iron and cast iron. Black iron’s malleability renders it suitable for applications requiring flexibility and structural integrity, such as beams in construction or metal framing.
Conversely, the high-carbon content in cast iron gives it excellent wear resistance, making it a favorite choice for heavy-duty applications. Therefore, it is commonly utilized in manufacturing engine blocks, cookware, and heavy machinery components.
Conclusion
In summary, while black iron and cast iron may seem similar due to their basis in iron, their manufacturing processes, properties, and applications significantly differ. Factories tailor their production techniques to optimize for either black iron or cast iron, responding to industry demands and leveraging the unique characteristics of each type. Understanding the distinctions between these materials can empower manufacturers and industrial stakeholders to make informed decisions, ensuring they select the right type of iron for their specific needs. This optimization not only contributes to the success of individual operations but also supports the broader fabric of industry by promoting efficiency and innovation.
-
High-Strength 3/4" Floor Flange | GPT-4 Turbo AI
NewsAug.05,2025
-
In Stock: 1/2" & 3/4" Galvanized Malleable Iron Floor Flanges
NewsAug.04,2025
-
Premium Black & Galvanized Key Clamp Fittings for Furniture Joints | Durable
NewsAug.03,2025
-
Wholesale China Malleable Cast Iron Decorative Floor Flanges
NewsAug.02,2025
-
3/4" Reinforced Bronze Flange Iron Pipe Floor Fitting | Threaded
NewsAug.01,2025
-
3/4 Inch Black Malleable Iron Floor Flange - Heavy Duty
NewsJul.31,2025