-
 Mail Usadmin1@hanghongtrade.com
Mail Usadmin1@hanghongtrade.com -
 Call Us+8613313271100
Call Us+8613313271100 -
language
Jul . 29, 2024 06:18 Back to list
Identifying Key Suppliers for Enhanced Elbow Joint Replacement Performance and Patient Outcomes
Understanding the Elbow Method and Its 90% Suppliers A Guide for Data Analysts
The elbow method is a widely used technique in the field of data analysis and machine learning for determining the optimal number of clusters in a dataset. This method is especially significant in unsupervised learning tasks such as clustering, where the goal is to partition a set of data points into groups based on their similarities. In this article, we will delve into the elbow method, what it involves, and its relationship with the concept of 90% suppliers—a term that often refers to the primary sources or providers of goods, services, or data that contribute significantly to a given context.
The Elbow Method Explained
The elbow method is primarily utilized in clustering algorithms, particularly k-means. The process involves the following steps
1. Clustering the Data The algorithm partitions the dataset into different groups based on a specified number of clusters (k). The analyst begins with a small k value (e.g., k=1) and gradually increases it.
2. Calculating Within-Cluster Sum of Squares (WCSS) For each k, the WCSS is calculated, which quantifies how tightly packed the clusters are. It represents the variance within each cluster; lower values indicate a tighter and more compact grouping.
3. Plotting the Results The WCSS values are then plotted against the number of clusters (k). As k increases, WCSS will typically decrease because adding more clusters will reduce the variance.
4. Identifying the Elbow Point In the plotted graph, the objective is to find the point where the curve starts to flatten, resembling an elbow. This point indicates that adding more clusters beyond this point yields diminishing returns in terms of reducing variance. Analysts typically choose this k value as the optimal number of clusters.
The Significance of the 90% Suppliers
elbow 90 suppliers

The term 90% suppliers often refers to the idea that a small percentage of suppliers account for a significant portion of the overall value or output in a certain supply chain or data ecosystem. In many industries, it is observed that approximately 80% of the effects come from 20% of the causes—a principle known as the Pareto Principle. Similarly, in a data analysis context, roughly 90% of the insights or valuable information may derive from a critical subset of data sources or suppliers.
By integrating the elbow method into supplier analysis, businesses can effectively streamline their data management processes. For instance, in identifying which suppliers contribute 90% of the value, analysts can cluster supplier data to segment them based on several attributes, such as cost, reliability, delivery time, and overall contribution to the business objectives.
Practical Applications
Utilizing the elbow method alongside the concept of 90% suppliers can lead to several practical applications
1. Supplier Selection Organizations can determine which suppliers to prioritize by clustering suppliers based on performance metrics and identifying the optimal number of clusters that represent various supplier categories.
2. Resource Allocation By focusing on the top suppliers that drive the majority of value, companies can allocate resources more efficiently, ensuring that strategic partnerships are nurtured, and potential risks are mitigated.
3. Performance Improvement The insights gained from clustering can inform decision-making processes related to supplier performance, driving improvements in supply chain management.
In conclusion, the elbow method serves as a powerful analytical tool, enabling data analysts to uncover the optimal number of clusters within datasets. When combined with an understanding of the 90% suppliers, businesses can enhance their decision-making strategies, streamline operations, and achieve greater efficiency in their supply chain management. By embracing these methodologies, organizations can foster a data-driven culture that underscores the importance of focusing on the major contributors to success.
-
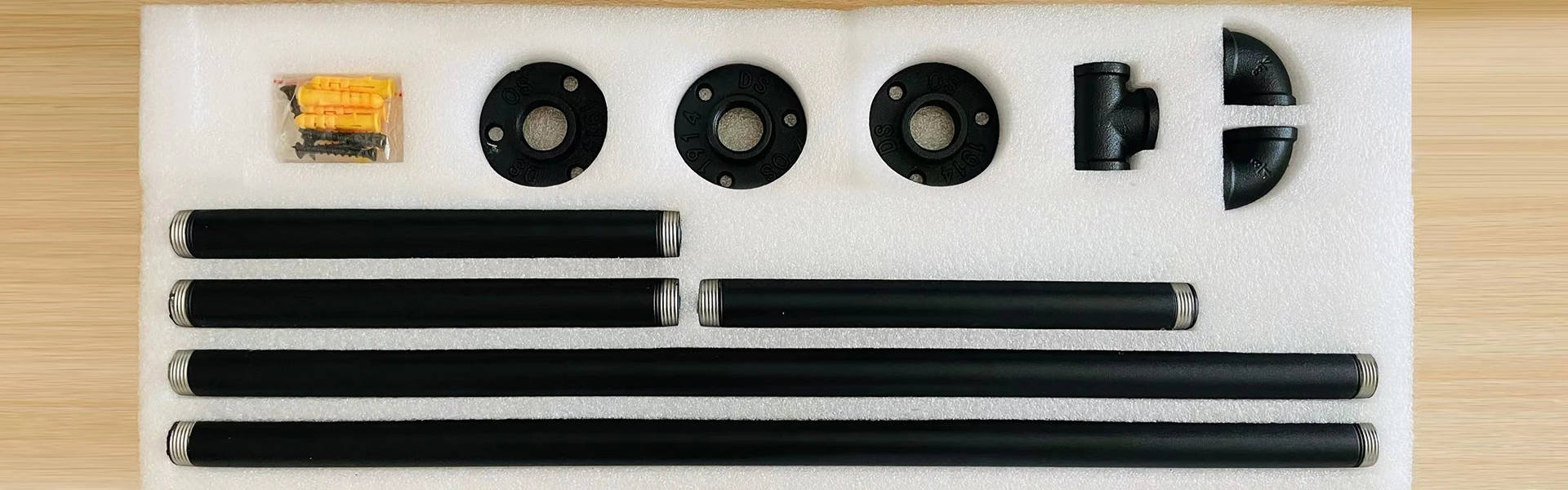
4X 3/4 Malleable Iron Pipe Fittings Floor Flange 3/4" Threaded BSP Wall Mount
NewsMar.07,2025
-
Galvanized 24yy 3/4"flange key clamp used for 26.9mm pipe
NewsMar.07,2025
-
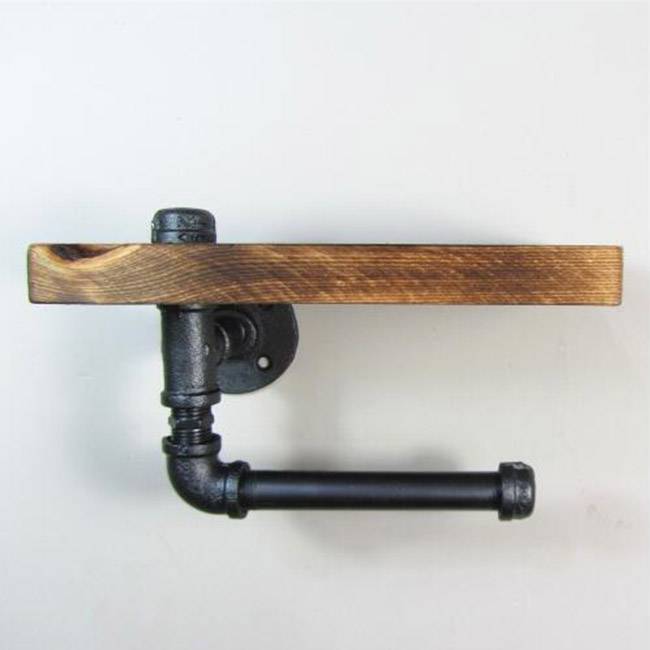
3/4inch malleable cast iron design plumbing pipe rustic industrial pipe shelf
NewsMar.07,2025
-
3/4'' black iron floor flange for plumbing pipe table
NewsMar.07,2025
-
Malleable Iron Pipe Floor Threaded Fitting Black Flange
NewsMar.07,2025
-
china brass pipe fittings
NewsMar.07,2025