-
 Mail Usadmin1@hanghongtrade.com
Mail Usadmin1@hanghongtrade.com -
 Call Us+8613313271100
Call Us+8613313271100 -
language
Nov . 08, 2024 11:00 Back to list
Comparing Black Iron and Cast Iron Manufacturing Processes and Their Advantages
The Comparison of Black Iron and Cast Iron Factories An Overview
In the world of metallurgy, two integral materials often come into conversation—black iron and cast iron. Both materials possess unique properties and applications that cater to different industrial requirements. Understanding the differences between these two types of iron can significantly affect production processes, costs, and product performance. This article aims to dissect the characteristics of black iron and cast iron, their manufacturing processes, and the implications for factories that work with these materials.
Black Iron Characteristics and Applications
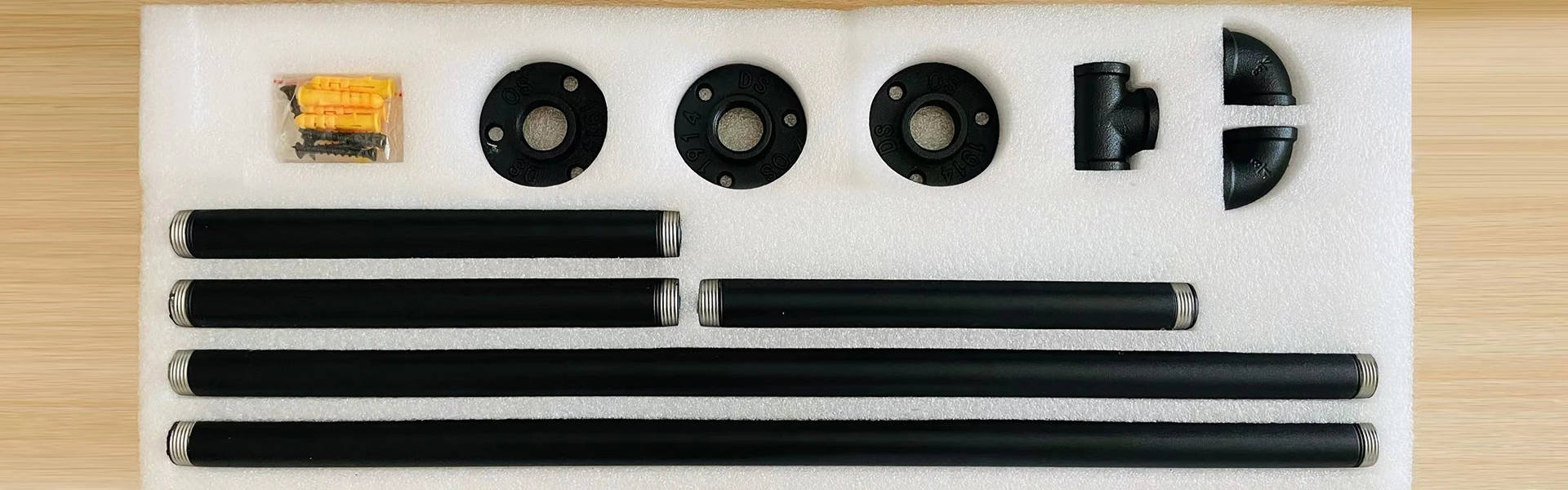
Black iron, often referred to as black iron pipe, is primarily used in plumbing and gas distribution systems. It is made from wrought iron or steel that is coated with a layer of black oxide, which provides resistance to corrosion. One of the defining traits of black iron is its strength and durability, which makes it highly applicable in structural applications. Additionally, it is malleable, allowing for easy welding and fitting.
The manufacturing process of black iron typically involves the continuous casting of steel, after which the material undergoes a heating and rolling process. Factories specializing in black iron production emphasize quick processing times and cost efficiencies. The target markets for black iron include construction companies, oil and gas industries, and manufacturers needing robust piping systems.
Cast Iron Characteristics and Applications
On the other hand, cast iron is a group of iron-carbon alloys with a carbon content greater than 2%. This alloying grants cast iron distinct properties, including high wear resistance, excellent casting capabilities, and good machinability. Cast iron can be categorized into various types, such as gray iron, ductile iron, and white iron, each with unique mechanical properties and applications.
The casting process for cast iron involves pouring molten iron into a mold where it solidifies, adopting the shape of the mold. This allows for intricate designs and structures to be formed, making cast iron particularly favored in the production of heavy machinery, automotive components, and cookware. Factories focusing on cast iron need to possess advanced casting technologies and equipment to maintain production quality and efficiency.
Comparative Analysis of Manufacturing Processes
black iron vs cast iron factories

When comparing black iron and cast iron factories, the manufacturing processes highlight both similarities and differences. Both types of iron typically undergo a smelting process where raw materials are transformed into iron. However, the subsequent steps diverge significantly.
Black iron production relies heavily on the properties of steel, thus emphasizing continuous casting and rolling techniques that favor structural formability. Machinery in black iron factories is tailored for high-speed processing and must maintain tight tolerances to ensure the integrity of piping systems.
Conversely, cast iron factories invest in advanced molding and casting technologies. The ability to create complex shapes necessitates innovative mold design and temperature control measures. Additionally, the cooling rate of cast iron must be meticulously controlled to avoid defects in the final product.
Environmental Considerations
Both black iron and cast iron production processes have significant environmental impacts. Factories must address emissions from smelting and casting, and increasingly, they adopt greener technologies to minimize their carbon footprints. The shift towards sustainable practices is crucial, given the scrutiny on industrial emissions and waste management.
Innovations such as electric arc furnaces (EAF) for black iron and improvements in the recycling of scrap iron are examples of how factories are adapting to environmental regulations while maintaining productivity. These measures not only help in compliance but also enhance the overall sustainability of iron production.
Conclusion
In summary, black iron and cast iron factories serve distinct roles in the metallurgical landscape, each with its own manufacturing nuances and market demands. The comparison between their production processes reveals not only the unique characteristics of each material but also the importance of adopting innovative technologies to address growing environmental concerns. As industries evolve, the competition between black iron and cast iron will continue to shape manufacturing practices and product applications. Understanding these dynamics is essential for stakeholders and businesses looking to leverage the advantages of either material in their production processes.
-
Heavy Duty 3/4" Industrial Pipe 'T' Shelf Brackets - Dark Grey Iron
NewsAug.27,2025
-
Black Floor Flange 1/2 for Furniture | Industrial Pipe Decor DIY
NewsAug.26,2025
-
Durable 1/2" 3/4" 1" Iron Threaded Floor Flange Wall Mount Pipe Fitting
NewsAug.25,2025
-
Black Malleable Cast Iron Floor Flange 1/2" BSPT, 3-Hole
NewsAug.22,2025
-
3/4 inch Black Finish Pipe Nipple for Home Decor & DIY
NewsAug.21,2025
-
3/4" Black Malleable Iron Floor Flange - Durable Pipe Fittings
NewsAug.19,2025